Digital and Health
Introductory information

Digital Transformation
What is it?
If you ask this question to different people or even the same at different time, you will get many different answers. You can look up a definition e.g. on Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_transformation) – you will still read a lot like “… it may ...” or “… some of these…” or “… using cloud technologies …” etc.
A brief description could be like: Improve the current status quo of a business by using new or complementary digital technologies to achieve current and future business goals more efficiently and sustainable. Efficiently can mean more than generation immediate revenue. The business takes the advantage of the fast developing technologies today and in the future.
What are good questions to answer at the beginning?
- Enhance the existing business digitally or create new digital business areas?
- Is my business focus still the same or is it becoming even a new IT business?
- Is my business getting obsolete soon or does it need a digital upgrade?
- Do I have the right resources to make the transformation happen?
- What would happen if I do not go for a transform?
- Etc.
How it works?
A transformation requires a holistic business and eco-system view to consider all dependencies between involved entities and stakeholder. The transformation is a technical and an organizational one with education, new roles, new skills, functions and communication paths etc. Fear and resistance are reduced by evolutionary changes. The buy-in and real backing from top-management and key stakeholder boosts the transformation speed. Initial pilots with focus on certain areas first reduces efforts and generates learnings for the next changes.
What are the major steps to take?
- Allocate resources. Resources are needed for each step. They can be internal, new or external resources. Important is to have the right skills and knowledge to cope with the tasks.
- Clarify the future needs and define business objectives to achieve.
- Be clear on the current status quo of processes, the involved stakeholder, the flows and the used digital technologies enabling the business.
- Use methodologies (Agile, Design thinking, change management, traditional project management, workshops etc.) as tools to identify the needed flows and processes to achieve the next and future business goals
- Identify how these processes can be supported or enhanced with digital technologies. Usually all identified objectives cannot be tackled at once or may be at all. Important is that the approach is clear and the (initial) expected result for each prioritized objective is named.
- Achieve the set prioritized objectives with execution of tasks with the right initiative / program / project. Pick the methodology or the mix of methodologies, which fits best.
- The organization is involved and transformed to live this for each ongoing or at least any new project. The initial transformation endpoint is the status quo before the next transformation.
Who needs it?
Any business from small to large business units should consider a digital transformation. Analysis of status quo and future objectives may indicate the scope of needed digital transformation.
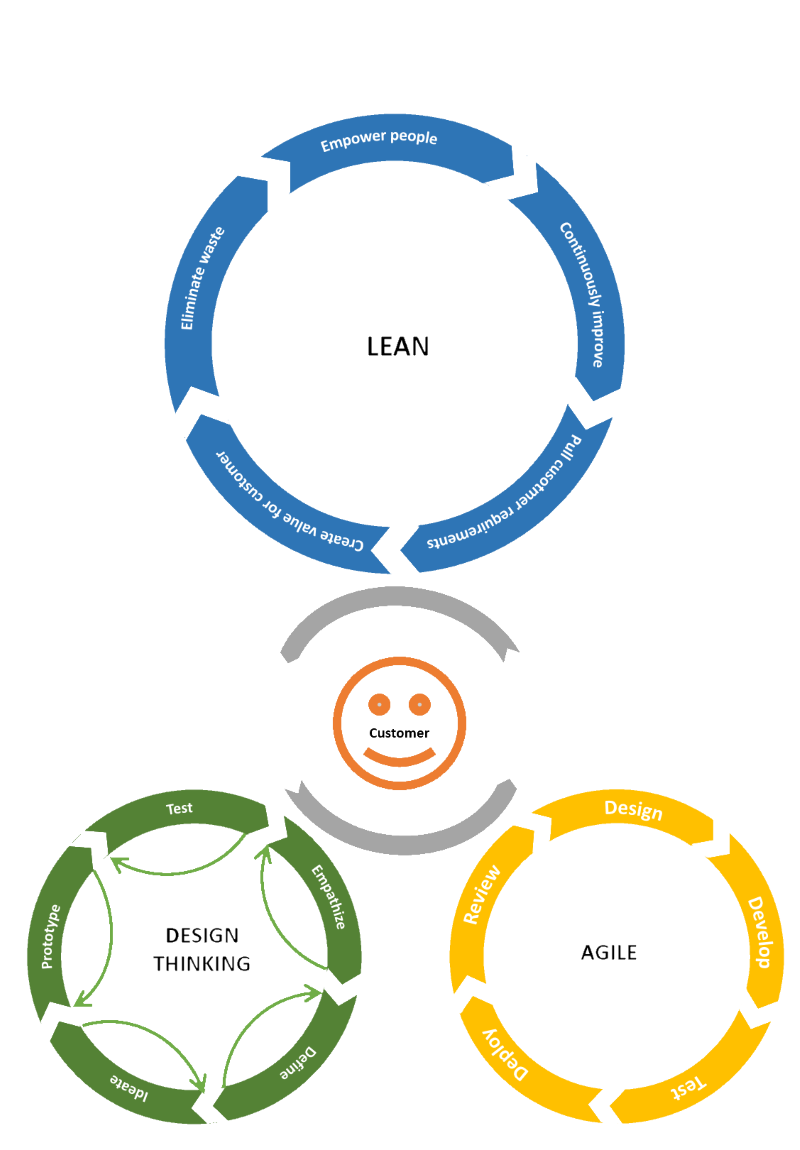
Methodology
The methods listed here are solution and result oriented and focus on satisfying customer needs. The customers can be internal or external. The use can be in the development of products as well as in the implementation of strategies. The methods may be applied individually or in combination. The orchestration of sharing unfolds the greater potential and can lead to significant change in an organization. The right choice of method (s) for each project is the key to success.
Design Thinking
The design thing process to the collaboration of users, designers and others. The process is iterative and flexible with the goal of realizing ideas that correspond to the nature of the real user.
The following basic steps help solve complex problems successfully and turn them into results. Due to the iterative approach, one or more steps may be repeated as many times as needed.
Understanding of human needs. (Empathy)
Reshaping and defining the problem in a human-centered way. (Humanistic problem definition)
Create many ideas in brainstorming sessions. (Brainstorming)
Easy and practical prototyping. (Prototyping)
Check if the prototype or solution solves the problem. (Testing)
Lean Development
Holistic approach in development with the aim of eliminating waste of resources
Recognize the value-generating process steps
Specify exactly the value of your product
Generate standardized uninterrupted value flow
Customer requirements determine content and timing of processing
Optimize things continuously towards perfection and free of errors
Involve employees, set clear goals, and develop them
Visualize the current status, recognize and decide the improvement steps together
Agile
Manifest (origin software development)
Develop software better and help others
Individuals and interactions are more important than processes and tools
Working software is more important than comprehensive documentation
Close cooperation with customer more is important than negotiation
Responding to change and not necessarily to the plan
Essential elements of the method are:
Incremental development & presentation of the interim result to the customer
Progress measure is the quantity of the functioning product
Close cooperation: subject matter experts and developers
Focus on simple as complex approaches
Regular situation analysis and adaptation of the procedure

Digital Health Eco-System
An eco-system covers more than one use-case. A system is composed of multiple units and if it is an eco-system all the units fits cohesively together. For the health area the digital units addressing and assuring the fit to the natural life flow. Business focus is on the customer with the eco-system around this individual. The eco-system and its dependent components can be defined within narrow borders or more wide. The wider it is the more complex and may be more sustainable business it will be.
Following areas may be the focus for digital enhancements considering human being as the customer in the area of interest in this eco-system. The target experience could be that all interactions and outcomes are easy, convenient, timely, streamlined, cohesive, and not perceived as extra effort.
Examples of Digital Health Solutions
- Mobile Health
- E-Patient Record / E-Health Record
- Tele-medicine
- Tele monitoring
- Virtual-HCP
- Digital assistants
- Cloud based services
- Bot, Chatbot
Examples of involved Stakeholder
- Human beings: Children, Women, Men, Other
- HCPs: Nurses, Doctors, Home Nurses
- Practices / Clinics / Hospitals
- Pharmacies
- Health insurances
- Medical Services
- Manufacturer
- R & D / Studies
Examples of sub-areas of a bigger eco-system
Home-Care
- Training and Education
- Hotline
- Connectivity Infrastructure
- Medical devices
- Communication tools
- Supply
- Home nurse services
Mental Health
- Mental training
- Mental assistance
- Mental test
- Meditation
- Relaxing
- Psychological support
- Chat and talk
Prevention
- Information
- Screening
- Nutrition
- Physical exercises
- Smoking weaning
- Stop Drinking
- Elderly monitor
Pregnancy
- Prevention
- Pregnancy
- Postpartum exercises
- Postpartum psychology
- Midwife assistance
- Kids care guides
Other topic examples
- Chronical Disease Management
- Acute Care
- Pregnancy
- Children Care
- Population Health
- Dental Care
- Drug management
- Rehabilitation
- Lab/Diagnostics

Articial Intelligence - AI
What is AI?
Technology mimicking intelligence / cognitive functions is called artificial intelligence. The focus is on the real outcome and not necessarily the detailed technical composition. The composition/architecture may be (very) different to biological reference. The human being is considered as the reference with highest known available cognitive capabilities.
AI in healthcare is not new, e.g. IBM did automated ECG interpretation already in the 1970s. The focus and enthusiasm on AI is growing enormously in all areas including healthcare. Advanced technologies building the foundation of growing digitalization. The easy access to digital technology by everyone and not just by professionals fuels the demand for AI based solutions.
How does AI work?
One of the most used technologies is machine learning. Artificial neural networks fed with pairs of data sets are trained with adjusting connections / synapses in that way that the pattern recognition is optimized to provide right output by having only the input values. One example of this kind is the use in radiology to interpret x-ray images, CT scans etc. Another model is to use decision trees to determine the output straight forward, e.g. by having symptoms and then concluding to the diagnosis of the underlying disease. There are many more ...
What are important considerations?
- It is key to determin the targeted output for an AI solution.
- Based on this selection determine the right model / technology to mimic the human cognitive function.
- Train and verify the AI solution with the right information / expert knowledge and comprehensive data sets.
- In medical area the right classification has to be declared and if needed the evidence of benefit to be shown.
Who needs AI Solutions?
Any business having specific competencies can enhance the own portfolio with AI solutions and improve their business resuls.

Health Data and Connectivity
Is standardization given?
Digital health bases on processing, interpreting, generating and transfer of data within one or between multiple health systems. The different health systems require connectivity with defined exchange and interface protocols. The more standardization is present the more independent and with less effort the respective health system can be developed and maintained. Over time, standards have been set at a technical and medical level. Especially the medical definitions of the standards are domain or modality dependent or may be undefined yet. The standards are evolving and maturing more and more. There is consensus on the need for further standardization. There is not one common organization, which is the owner or leader of the standardization for health information exchange and ensuring interoperability.
There are 3 levels of interoperability identified from the European eStandards consortium for health information exchange:
- Technical - data security, privacy, integrity, access privileges
- Semantic - understanding about the same meaning of the information / data
- Organizational - ability and willingness to exchange information based on laws, policies and cooperation agreements.
Few examples of broadly used Medical Standards are:
- HL7 (different versions and capabilities from version 2.x to FHIR) from Health Level 7 International. The later versions is considering more and more ontologies and domain related information.
- LOINC from Regenstrief Institute - provides universal codes and names that provide the global common language for identifying tests and observations.
UCUM from Regenstrief Institute - The Unified Code for Units of Measure is a code system intending to include all contemporarily used units of measures to facilitate unambiguous electronic communication internationally – bases on ISO 80000 standards parts 2-14 above. - ICD-10 / ICD-11 from World Health Organization (WHO) - Disease classification

